Click here for an excerpt from the 1963 book Satellite Communications Physics that describes the method and mathematics for determining the orbit of a satellite.
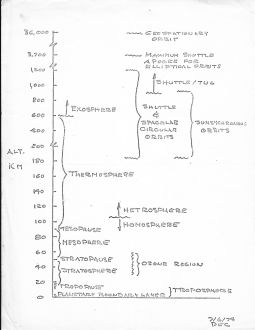 A single chart showing relative altitudes of the atmosphere and satellite orbits.
A single chart showing relative altitudes of the atmosphere and satellite orbits.
Global Positioning System
Satellite Radio
Determining Satellite Orbits
Little LEOs
Big LEOs
Broadband systems
Imaging
Military Satellite Systems
Glossary
Vulnerabilities
All satellites are controlled by a coded tape.
The trick is, of course, to have the right code.--Ernst Stavro Blofeld, Diamonds are Forever, 1971
| Click here for information related to the U.S. Department of Defense Navstar Global Positioning System, better known as GPS. |
|
Notes on the
XM Radio
Sirius Satellite Radio
WorldSpace Prime Rate channels are 16 kbps. The satellite payload was designed by Alcatel in Toulouse, France. L-band transmit power is from a pair of 150 watt TWTs. Broadcasters access the satellite via FDMA uplink in X-band between 7025 and 7075 MHz. The uplink capacity is 288 Prime Rate channels. The satellite demodulates each uplink and combines them into a TDMA downlink at L-band.
|
|
A good page describing orbital mechanics can be found
here.
Click here for an excerpt from the 1963 book Satellite Communications Physics that describes the method and mathematics for determining the orbit of a satellite.
|
Little LEOs are constellations of low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellites that provide data services in the VHF bands. The first in service and currently most active Little LEO is Orbcomm.
The Federal Communications Commission has granted licenses to five Little LEOs.
Big LEOs are constellations of low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellites that provide voice (and now data) at frequencies above 1 GHz. Iridium and Globalstar are the two largest and most active systems.
In October 2002 Teledesic suspended satellite construction and laid off a number of employees. Earlier in 2002 Teledesic had contracted with Alenia Spazio to build 2 of the 30 medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites.
[Prior to 2000]
A Saudi Arabian prince with an estimated net worth of more
than $11 billion has investmented $200 million
in the 288-satellite
Teledesic
system. Alwaleed bin Talal, who currently owns part of
Netscape and
Motorola, joins billionaire
cellular pioneer and current CEO Craig McCaw
and Microsoft Chairman Bill Gates in funding
the planned "mega-LEO."
Major shareholders:
| McCaw | 30% |
| Gates | 30% |
| Alwaleed | 16% |
| AT&T Wireless Services | 12% |
Teledesic, which has received authorization from the FCC for it's planned high-bandwidth satellite network, has already launched a test satellite but remains tight-lipped about their technical progress.
Boeing is slated as the prime contractor, having won a contract worth an estimated $9 billion. Boeing will sink $100 million of its own into Teledesic, gaining a 10% share of the "Internet-in-the-sky" company. Boeing has been busy lately, merging with McDonnell-Douglas after completing the purchase of Rockwell's Defense Electronics group.
SkyBridge is another broadband hopeful.
| SYSTEM | MAJOR BACKER(S) | ORBIT | SATS | WHEN | Uplink | Downlink |
| Iridium | Motorola | Big LEO | 66 | September 23, 1998 | ||
| Globalstar | Loral, Qualcomm | Big LEO | 24/48 | 1999 | ||
| Odyssey COMBINED WITH I-CO |
TRW | Big MEO | 12 | 2000 | ||
| I-CO | Inmarsat | Big MEO | 10 | 2000 | ||
| Orbcomm | Orbital Sciences Teleglobe |
LEO | 48/20 | twelve now | 148 - 150 MHz | 137 - 138 MHz |
| VITA | Volunteers In Technical Assistance | Little LEO | two | 148 - 150 MHz | 137 - 138 MHz | |
| LEO One | LEO One USA | Little LEO | 148 - 150 MHz | 137 - 138 MHz | ||
| E-Sat | Echostar Corporation | Little LEO | 148 - 150 MHz | 137 - 138 MHz | ||
| Starsys CANCELLED |
GE | L-LEO | 24 | 1998 | ||
| Teledesic | Microsoft, McCaw, Boeing | L-LEO | 200 | |||
| Ellipsat | Ellipso | LEO | 16/24 | |||
| Elekon | foreign | LEO | 28 | partial now | ||
| Gonets | foreign | LEO | 24 | partial now |
Notes:
Click here for an interesting composite of earth at night.
Defense Meteorological Satellites Program
Click here for the home page.
Updated November 2, 2002